Latest anti-cheat technologies in eSport: how the industry fights the invisible enemy
Author: Hawk Live LLC
Last updated:

Cheating is considered one of the most serious problem of modern cybersports disciplines, which does not lose relevance, despite the active measures to combat this type of cheating. The possibility to simplify or automate the game process attracts not only players who want to gain an advantage over their opponents, but also cheaters who try to make money by selling accounts and game items. In this article, let's look at what technologies are used by developers of modern online games to combat cheating.
The most common methods of cheating
Let's consider the most common methods of cheating in modern online games, and analyze their main features.
Method | Feature | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Aimbot | A cheat program that “aims itself” and guarantees hits to the head or body of the opponent without the involvement of the player's hand. With such a development, the player instantly becomes an accurate shooter, even if he can not see the enemy through cover. | ||
Wallhack | This is a modification of the client part of the game that allows you to see your opponents through walls and terrain. | ||
Speedhack | A cheat that changes the speed of the player's actions - from super fast running to super slow pauses. | ||
Scripts and macros | Semi-automated combinations of actions - rapid fire, automatic series of blows and combos. Although they are less visible to anti-chit technology, scripts simplify complex techniques (rapid fire, pressing multiple keys), which also allows you to gain an advantage over your opponent. | ||
Vision hack | This cheat is widely used in MOBA games. It allows you to immediately see all the movements of your opponents. | ||
Boosting | Although technically it is not a software, but a service, “boosting” an account is also considered a form of fraud. It often involves the use of various vulnerabilities to speed up the process of rating boosting. | ||
How anti-chit technologies have changed
The start of the development of anti-chit-systems fell on the early 2000s, when developers began to implement simple memory scanners in games, looking for known signatures of cheat programs. An example of such software is the PunkBuster program, which searched for modified game objects in memory. Notably, the technology was updated until 2015 and was used in many popular online shooters.
In 2002, Valve first implemented the VAC (Valve Anti-Cheat) system in CS and Steam, which is updated by the company to this day. By 2006, this software detected tens of thousands of cheaters per week, but such results were not enough to effectively combat the problem, so the developers began to use more advanced methods, such as
server reconciliation of player actions (FairFight);
replay evaluation;
monitoring of the player's hardware at the driver level.
Riot Games implemented its own Vanguard anti-cheat client and driver at the kernel level, and Epic/Valve started to actively integrate solutions like EasyAntiCheat and BattleEye, but by the early 2010s it became clear that these technologies were no longer able to cope.
As of 2018, Valve implemented machine learning by creating the VACnet neural network, trained on thousands of identified instances of cheating through the Overwatch system. VACnet now looks at 150,000 CS:GO matches per day, which has increased detection rates from 15-30% to 80-95%.
Developers vs. cheaters: how technology development affects the number of infringers
Below are graphs illustrating the dynamics of cheating in Dota 2, CS(2) and League of Legends according to open source data.
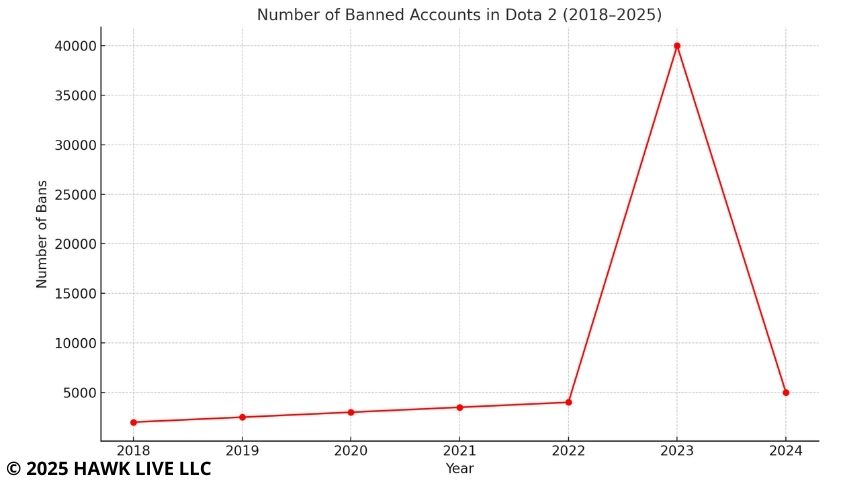
The graph shows the number of accounts banned by Valve for using cheats in Dota 2 according to IGN. The obvious anomalous peak was in 2023, when developers claimed more than 40,000 banned cheaters in a matter of weeks. In comparison, previous years, major waves of bans in Dota 2 were barely mentioned in official reports. This indicates that the massive anti-cheat operation launched in early 2023 has drastically reduced the number of cheaters.
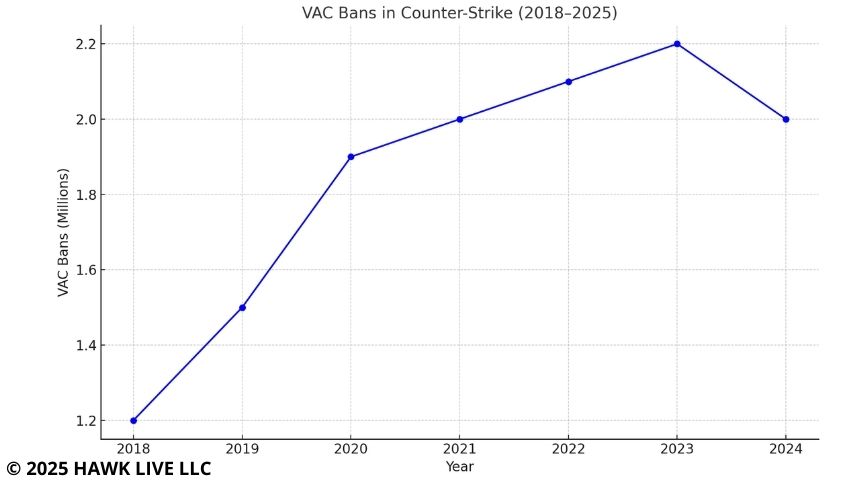
The graph, based on material from Steamcommunity, shows an estimate of VAC bans in the Counter-Strike series. In 2018, there were over 1.2 million VAC bans, and by 2020, that number has surpassed 1.9 million. This means that the number of players caught cheating has continued to rise. It's interesting to note that it was in 2018 that Valve introduced VACnet (machine learning for cheat detection) and in 2020 added Trusted Mode, but the graph shows that the total number of bans didn't decrease - rather the opposite, it increased slightly. This shows that despite the improvements in anti-cheats, the percentage of cheaters in CS:GO/CS2 remains high, however, it also confirms that the effectiveness of modern systems is increasing.
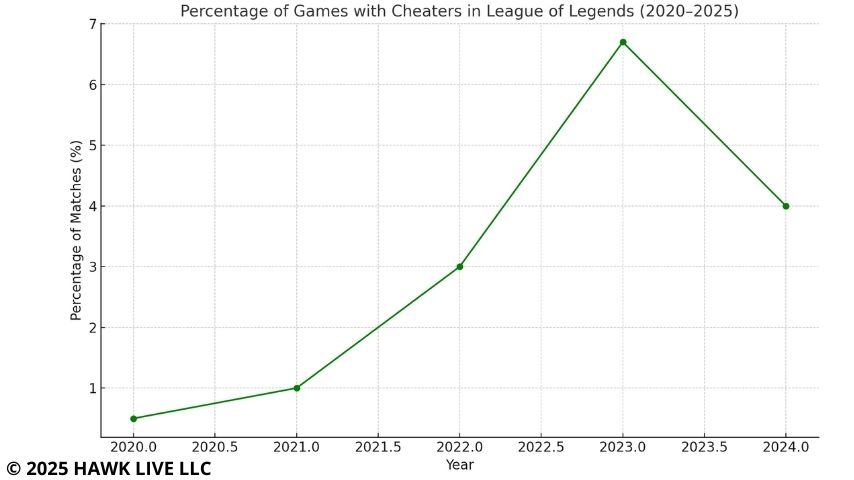
The graph, based on data from the official League of Legends website, shows the approximate proportion of matches with at least one cheater. According to Riot, in the beginning of 2024, approximately one in every 15 matches had a cheater (about 6.7% of games). You can also see a sharp increase from 2021 to 2023, corresponding to an increase in the number of detected infractions in the LoL community. Most alarmingly, in 2023, more than 10% of top-ranked (Master+) games also involved cheaters. The drop in 2024 is due to the introduction of Vanguard and bot filters.
Cheating in cybersport: scandals and high-profile revelations
Despite powerful anti-cheat solutions, high-profile cases with cheaters regularly pop up in ESPN Publishing news. Let's take a look at high-profile scandals due to cheating in cybersports.
In 2018, during the Asian CS:GO Championship, the game was suspended when admins discovered that OpTic India team player Nikhil “Forsaken” Kumawat had enabled a pre-installed cheat right during a match.
After a lengthy investigation, Riot discovered that during the Riot Games Game Changers women's tournament, participant Madelyn “malibu” Campos was playing with someone else's account and circumvented the total hardware ban by using a new PC and account. As a result of the investigation, Riot permanently suspended both suspects from any competition.
Following the Chinese DPC Dota 2 event in early 2023, Valve banned 46 players (including the entire Knights team) for suspected “interference with fair play”, some of the bans were indefinite.
In 2020, ambitious amateur VALORANT Phox was banned for life by Riot for playing with cheats. He later pleaded guilty.
AI on the guard of fair play: modern solutions
In 2025, the effectiveness of anti-cheat technologies has increased significantly due to the introduction of AI in anti-cheat systems. Valve's VACnet technology analyzes the behavior of players in tens of thousands of matches every day, and constantly improves the detected patterns of cheat programs. The system has learned to accurately detect the use of aimbots by evaluating the trajectory of the aim. Moreover, the developers have started to separate suspected cheaters and honest players from each other, which improves the quality of games for honest players.
Vanguard from Riot Games is keeping pace with its competitor from Valve. The system is active at all times when one of the developer's games is running on the user's PC. The software scrutinizes all game processes, detecting suspicious activities.
Now Tencent is actively working on the development of Anti-Cheat Expert (ACE) technology, and its engineers are already demonstrating deep models that analyze player behavior by recording games. According to the company, ACE provides 24/7 monitoring and real-time data processing, instantly identifying unscrupulous players. At the GDC-2025 conference, Tencent specialists talked about deep neural networks that “study” replays and identify characteristic signs of cheats in the game.
Conclusion
Industry leaders demonstrate zero tolerance to cheating. Developers not only strictly punish unscrupulous players, but also actively develop technologies to detect cheating, which significantly complicates such manipulations in online games. What do you think, is it possible to completely defeat cheaters?








