From punks to Metaverse: how the NFT market has changed over the past 5 years
Author: Hawk Live LLC
Last updated:

Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, have become a significant investment vehicle that has experienced growth, falling demand, and format transformations in recent years. In 2022, large companies and brands turned towards the market - Starbucks, Nike, Reddit and even Gucci - and it all started with harmless collections of pictures.
Let's remember how it was and what NFTs have gone through to get to the current point.
Early NFT years
The first non-fungible tokens began to appear even before 2017 - then they were experimental projects, not very similar to today’s NFTs. The first closest prototype of what we can observe today was the Etherea project, which proposed the concept of buying digital plots on the blockchain.
In 2017, when NFTs were still not very popular, the Larva Labs team developed the concept of cryptopunks – a unique, randomly generated collection of digital pixel art. The developers had to work hard to get the attention of the audience: they managed to achieve this only after the publication of Mashable, which was released in June 2017. Then 9,000 punks were given away for free, and those that were sold cost very little – up to $1.
Interest in non-fungible tokens began to grow in 2018 and gradually increased by 2020 - this can be seen in the increase in the number of active wallets on the market. The dynamics is clearly demonstrated in the report of the NonFungible.com information and analytical platform dedicated to the NFT market.
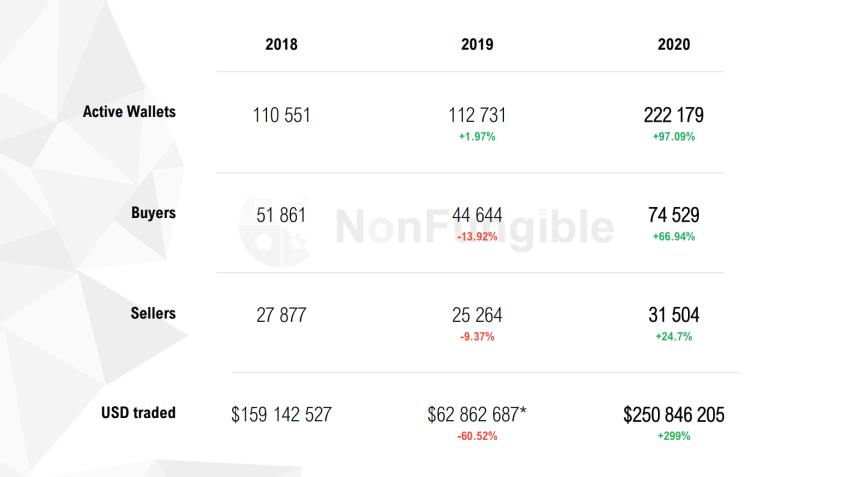
Source: NonFungible 2020 report
From the same report, we can see how much capitalization of the sector has grown. In 2018, it was only $40.9 million, and in 2020 it exceeded $338 million:
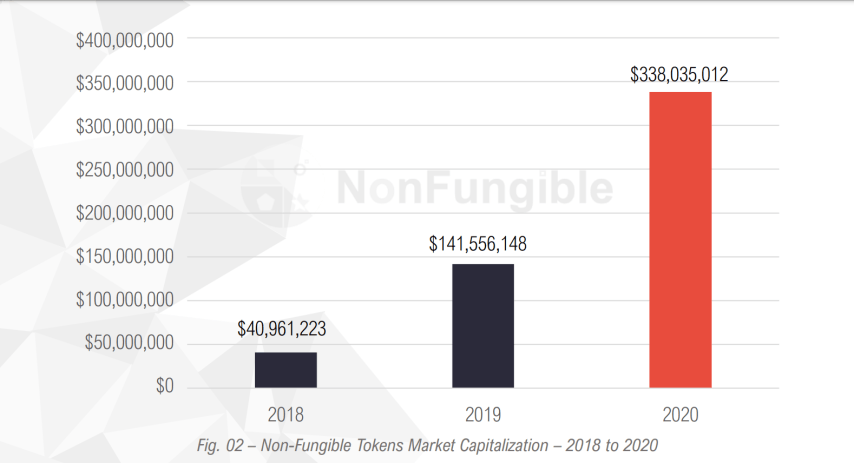
Source: NonFungible 2020 report
By 2019-2020, the Play to Earn games known to us today began to appear on the market - first of all, Axie Infinity, which held several successful funding rounds and raised $159 million plus 4,100 ETH from venture investors. The project was not yet in such demand among the audience - during the public auction that started on November 4, 2020, a modest $2.9 million was raised. The Sandbox project was launched on the market in the same year.
Launched in 2017, Decentraland has long allowed universe participants to buy NFT lots for as little as $20 due to relatively low demand.
NFT and Digital Arts: 2021-2022
The first jump in the popularity of NFT took place in 2021. The easiest way to track this trend is to study users’ intents: Google Trends open statistics over the past five years clearly show how the number of requests jumped for the first time in the spring of 2021:
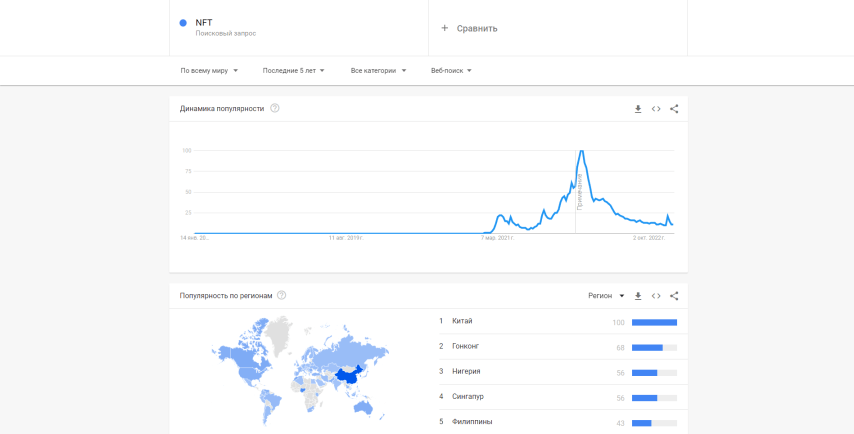
Google statistics for the query “NFT”
Research suggests that the sudden interest in the topic is due to the rise in the value of Bitcoin and the capitalization of the entire cryptocurrency market in early 2021. Indeed, it was during this period that digital gold began to reach historical highs:
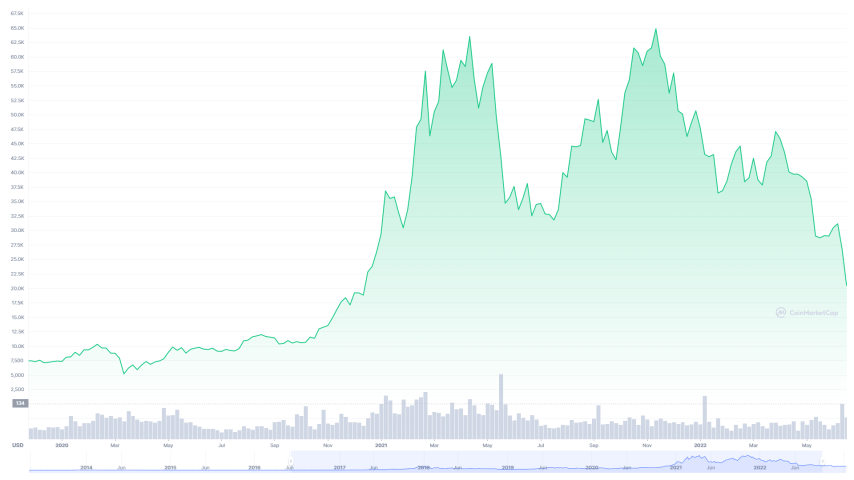
Bitcoin, 2021
During this period, the GameFi sector was actively developing, but the main focus was on digital art. Statistics from Scientific Reports show a significant gap between sectors in 2021:
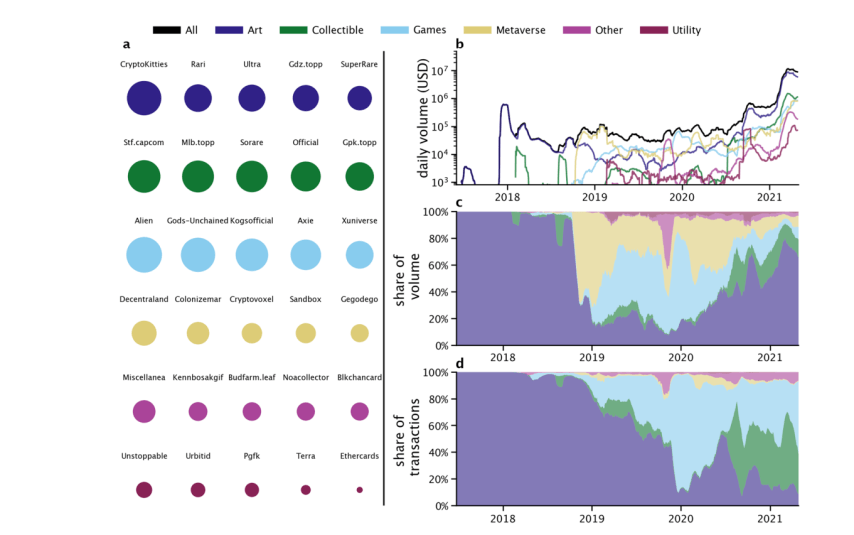
The main trading platform for creating, buying and selling NFTs has become the OpenSea marketplace. There were other auctions on the market, where expensive transactions were carried out daily - it was in 2021 that these tokenized paintings were sold:
- CryptoPunk 3100, $7.58 million
- Everydays - The First 5000 Days, $69.3 million
- CryptoPunk NFT 4156, $10.2 million
- Yuga Labs, Bored Ape Yacht Club 8817, $3.4 million and others.
Not only digital images were sold. Kanye West digitized and sold an album of his unreleased songs, and at Sotheby's auction in 2021 they put up for sale the WWW browser code with the original file archive of author Sir Tim Berners-Lee.
Due to the unprecedented demand and growth in the value of tokens, the NFT market reached $15.5 billion in 2021. The trend slowed down in 2022 – according to the same Google Trends data, users’ interest in NFTs increased strongly in January and then began to subside.
However, it is not all that bad. Forbes published the results of 2022, which collected interesting numbers:
- The capitalization of NFT collections reached $35 billion in March ($21 billion at the end of the year) against $21 million at the beginning of 2021;
- Weekly trading volume peaked at $1.3 billion vs. $26 million in January 2021.
NFT and GameFi
GameFi, which consists of Play to Earn and Play and Earn games, received slightly less attention than digital art, but also showed significant growth. Some experts believe that 2021 was a transitional year for the market, and then non-fungible tokens experienced a slow but sure metamorphosis from ordinary collectible items to more complex virtual objects.
Developers managed to attract $3.3 billion in 2021. In 2022, interest in NFT games and their audience began to fade. This became especially noticeable in the example of Axie Infinity, which was hacked in March - however, the decrease in the active audience began even before that.
NFT and Bitcoin
It is impossible not to pay attention to the relationship between non-fungible tokens and digital gold. NFTs will not replace Bitcoin as they are in a different category of assets and perform different functions. But the rise and fall in the popularity of NFTs correlate with changes in the Bitcoin dominance index.
The Bitcoin dominance index displays what share the asset occupies in the market in a specific period of time. In 2011, when the currency had no competitors, the ID indicator was tending to 100%; as the industry developed and new projects appeared, it began to decline.
The index is calculated as the ratio of BTC capitalization to total market capitalization, sometimes multiplied by 100% for convenience. To track this indicator, there are special charts where you can see the dynamics in recent years and compare it with significant events in the market:
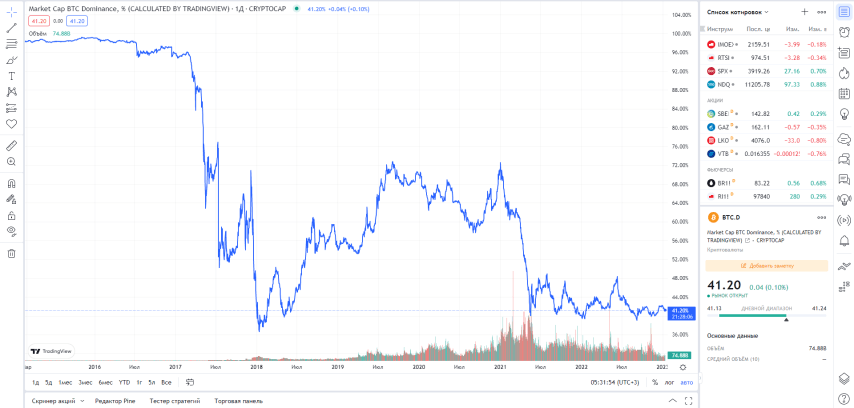
Bitcoin Dominance Index, Tradingview
In March 2021, as the price of BTC began to rise, as well as the market share of NFTs, the dominance index began to plummet. At the end of April 2021, the indicator fell for the first time to less than 50%, and in May to 39.9%.
This is directly related to the growing popularity of NFTs in the arts and blockchain games that use NFTs, both of which use altcoins for transactions. When the importance of the sector began to rise, so did the demand for altcoins. And where there is increased demand, there are rising prices and increasing capitalization. The greater the capitalization of altcoins, the less Bitcoin dominates.
Bearing in mind such a relationship in the market, collectors and investors can choose the best moments for investments and invest profitably when altcoins become cheaper.
What's next for NFTs?
In 2022, the main trends emerged in the cryptocurrency market, which will develop in the next few years. They are Web 3.0 and Metaverses as its integral component.
The main feature of Web 3.0 is that no one can give a precise definition of this term. Web 1.0 has been classified only after Web 2.0 and the significant differences between them, and it is still difficult to predict what exactly the Internet of the future will be like. It is reliably known that blockchain and DeFi will become its integral part, because the main principles of Web 3.0 are:
- Full control in the hands of users;
- Freedom and openness;
- Lack of censorship.
The virtual world of the Metaverses will also find its place in the new Internet - perhaps this trend was set by the Covid-19 pandemic, which showed the need to actively move into the online environment. And perhaps the coronavirus has only accelerated this already inevitable process.
Metaverses give humanity almost unlimited possibilities, some of which have already been implemented in existing projects. This is the purchase of digital land, communication, joint sports and even work. NFTs will play a decisive role in this virtual world - in fact, it is the only tool that allows you to identify digital objects and effectively assign ownership to users.
Criticism of the NFT
Today, NFTs are also being criticized from a technological standpoint. The main stumbling block was the issue of security and reliability of such digital assets. We found a study explaining what risks non-fungible tokens can carry as they exist today. Brief conclusions:
- NFTs linked to domains on the Web may become invalid when the domain disappears and lose their value;
- Attackers have tools to bypass saving transaction records in the blockchain;
- Merchants using cross-platform trading solutions may evade paying royalties to NFT creators.
These are the main disadvantages that can make working with NFTs unsafe and threaten financial losses. So far, the industry is at the stage of development and has not revealed its full potential - it can be assumed that over time, as non-fungible tokens are popularized in new areas of application, all these shortcomings will be corrected.
Conclusions
NFTs already existed 8 years ago, but the audience needed some time to understand this concept. Once the popularity of non-fungible tokens was associated with the growth of Bitcoin and also influenced it, but as the sector matures, the demand for it will no longer be provided exclusively by digital gold.
Now society is in a transitional stage, when the functionality and capabilities of tokens will expand and go beyond the scope of ordinary collecting.








