The eSports of the future is already here: how VR and AR are conquering arenas
Author: Hawk Live LLC
Last updated:

Just imagine: you put on a VR headset and find yourself not in a room, but in the center of a virtual stadium. The crowd roars around you, a giant dragon circles over the arena, and you literally feel the tension of the match. This is no longer a fantasy - this is the new reality of cyber sports. In this article we will look at how VR- and AR-technologies are used by the organizers of cyber sports tournaments to increase the interest of spectators.
What are VR and AR, and how do they work in broadcasts?
In modern cyber sports, virtual (VR), augmented (AR), mixed (MR) and augmented (XR) realities significantly increase the interest of viewers due to the presence effect. Let's consider and compare each of the technologies used by tournament organizers in more detail.
Virtual reality (VR) immerses the viewer in a fully computer-generated virtual world through the use of special VR glasses.
Augmented reality (AR) superimposes digital elements on the real world, which the viewer sees through the screen of his gadget or special AR-glasses. These can be images, text or 3D objects that complement the perception of the surrounding reality.
Mixed reality (MR) combines elements of VR and AR. MR devices allow you to see the real world but overlay it with interactive virtual objects that look and behave as part of reality.
Augmented Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that combines all the technologies mentioned above, as well as any future innovations that may alter our perception of reality through digital means.
In the context of cybersports, the main three tools of augmented reality allow for different forms of audience interaction:
VR takes the viewer inside a virtual arena or game world.
AR extends the broadcast by adding interactive elements on top of regular video.
MR allows you to create interactive events where virtual elements interact with the real audience or environment.
Characterization | Virtual Reality (VR) | Augmented Reality (AR) | Mixed Reality (MR) | Augmented Reality (XR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Main idea | Total immersion in the created digital environment | Adding digital elements to the real world | Integration of virtual objects into the real world with interaction | A term that combines VR, AR and MR, as well as any future technologies that may change the perception of reality |
Equipment | VR goggles, headphones, sometimes controllers and other sensors | Smartphones, tablets, AR glasses | MR headsets (e.g. HoloLens) capable of spatial scanning | VR headsets, AR glasses, MR headsets and future similar devices |
Interaction | Full sense of presence in a virtual world | Interaction with digital objects superimposed on reality | Interaction with virtual objects fixed in real space | Interaction in fully virtual, augmented or mixed environments |
Cyber sports applications | Virtual stadiums, 360-degree immersive broadcasts | Interactive elements on broadcasts, AR filters, real-time statistics | Virtual elements in real arenas (e.g. holograms, interactive projections) | Covers all of the above applications and future innovations |
Augmented reality for players and viewers in the meta universe
One of the most exciting applications of virtual reality in eSports is the creation of virtual stadiums and fan zones. VR technologies immerse spectators in the atmosphere of large-scale events right from home, instead of a person's physical presence in the arena. This approach allows every cybersports fan to feel their presence at an event from anywhere in the world without the physical limitations on audience size that characterize real stadiums. Let's take a look at the most famous augmented reality technologies in eSports.
Title | Description |
|---|---|
ZENOS Stadium is an immersive Virtual Space that is available for PC, AR and VR device users. The platform allows millions of spectators to connect to events simultaneously, creating the effect of being in a real stadium. | |
EVA (Esports Virtual Arena) | A company from France that builds physical VR arenas where players take part in matches in full virtual reality format, and spectators get the opportunity to watch the action, both live and with the help of online connection through a VR interface |
The technology developed by Phenomena works on a similar principle, providing modular VR spaces adaptable to different competition formats. A virtual fan space is realized for spectators, where they can not only watch the event, but also interact with the virtual environment. | |
Previously, the technology provided a virtual presence at live eSports events. Despite the closure of the project in its original form, the technology behind it continues to evolve and integrate into new meta-universes and VR ecosystems. |
The virtual presence provided by the aforementioned technologies gives the viewer a strong emotional impact through a highly immersive experience. Unlike standard broadcasting, there is an opportunity not only to observe the players' actions closer, but also to choose any non-standard angles and move around the virtual arena, feeling a strong involvement in the events taking place.
How VR/AR increases audience engagement and retention
The integration of virtual and augmented reality technologies into eSports broadcasts has a significant impact on increasing audience engagement and time spent interacting with content. Research by Hanene Hammami of International Review of Management and Marketing (2025) shows that the use of VR in gaming environments contributes to a significant increase in user satisfaction through active engagement and multi-sensory interaction. Engaged users are more likely to return to content, which is critical for audience growth and monetization of cybersports broadcasts.
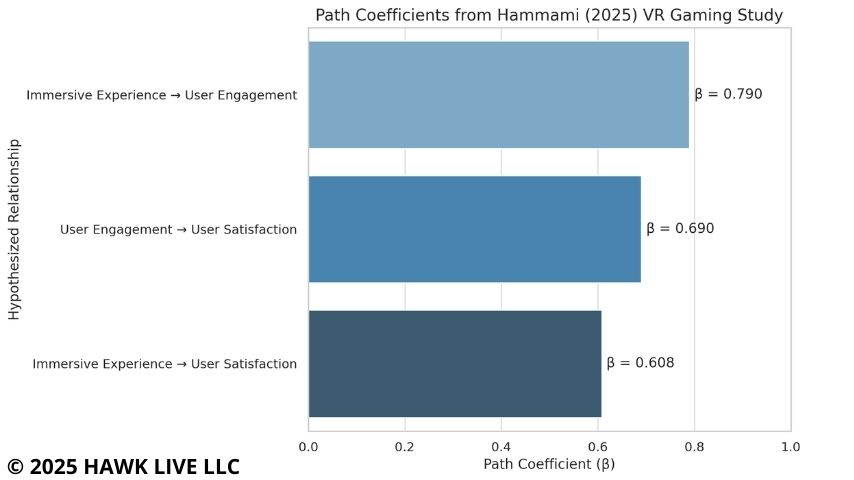
β is a standardized coefficient that shows the strength of the influence of one phenomenon on another. The closer this coefficient is to one, the higher the level of correlation. The influence is considered strong if β is greater than 0.5. From the results we can conclude that the more the player feels “inside” the game (immersiveness), the more he is involved. The more he is involved - the more satisfied he is. And even immersiveness itself also significantly increases the pleasure of the process.
In addition, according to RockPapeRreality, AR filters and masks are actively used by fans to express support for their teams. This approach leads to increased reach on social media. According to the authors of the study, publications with AR content show up to 70% higher organic reach compared to regular visual content. Thus, AR not only strengthens the emotional connection to the event, but also contributes to the growth of the broadcast audience due to the viral effect in the digital environment.
It can be concluded that the use of augmented reality technologies in cybersports allows creating a new format of interaction with the audience, where the viewer turns into an active participant of the events. This approach not only improves the viewer's experience, but also makes the event more viewable, which increases the income of the organizers.
Bright cases of XR technology application in cybersports
For the sake of clarity, let's take a look at the most high-profile examples of the use of XR technology in eSports that left a vivid impression on the audience.
Event | Description |
|---|---|
Opening of the League of Legends 2017 World Championship Finals | During the performance of Against the Current with the song Legends Never Die, a huge virtual dragon appeared, interacting with the surrounding environment. The moment caused excitement and became a viral example of AR's potential. |
WePlay AniMajor | According to Forbes, the organizers used AR and XR technologies with the help of the Pixotope platform: the game characters and the stage were complemented with virtual anime decorations, creating a feeling of total immersion. |
Games of the Future 2024 | Participants competed in fijital formats (a blend of physical and digital activity) using VR, AR and wearable devices. |
AIC 2020 Grand Finals | Spectators had access to an AR interface with 3D maps, game stats and avatars displaying real-time data. |
What's next: the future of eSports in VR and AR
As the authors of Medium predict, augmented reality technologies will take a key role in the future of cybersports, transforming it into a more immersive and personalized show. The authors predict the emergence of full-fledged cybersports tournaments that will take place entirely in virtual reality. and viewers will be able to watch the action from the first person.
According to the Esports Trade Association, augmented reality technologies are transforming the fan experience at live events by integrating holograms, dynamic AR screens and real-time personalized information layers.
The GlobeNewswire report also highlights the rapid growth of the VR market and its significant impact on the entertainment industry. Interactive fan zones in meta-universes where viewers can watch matches together, participate in mini-games and interact directly with content are predicted to be actively created. All of this is shaping a new generation of cybersports - more immersive, social and accessible.
Conclusion
Augmented reality technologies are actively transforming from experimental to the accepted norm, expanding interactive opportunities and ways of interacting with audiences. Organizers of cybersports events are actively using virtual and augmented reality technologies to increase audience interest, and in the future, the integration of such technologies into cybersports, according to most predictions, will only increase.








